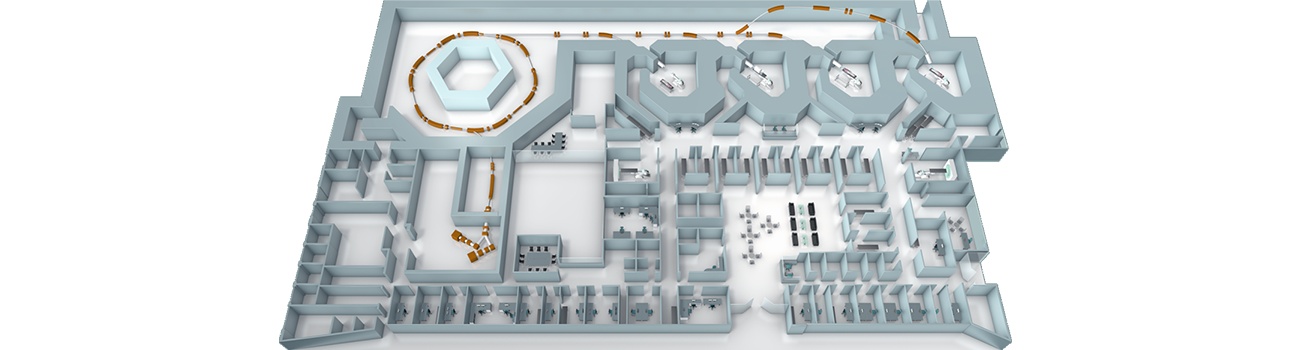
Accelerator facility
In the context of particle therapy, the radiation is performed with protons and carbon ions. The pathway of the ion beam in our particle therapy facility from the generation of the beam to the effect in the patients is explained in the following paragraphs.
1. Ion sources
1. Ion sources
The generation and first acceleration of the particles is performed in the ion sources, one for protons and one for carbon ions. Gas molecules are transformed into positively charged atoms, so-called ions. To gain protons, hydrogen gas is used and to gain carbon ions, carbon dioxide is taken. The ions are then extracted with a high voltage of 24 thousand Volts, accelerated, and separated in the following beam guidance so that an unmixed beam is generated. The beam transport occurs in a vacuum like in the other parts of the accelerator in order to avoid beam losses.

2. Linear accelerator
2. Linear accelerator
The second part of acceleration consists of two high-frequency acceleration steps. In these so-called cavities, high-frequent electrical fields ensure the acceleration of the beam to about 12% of speed of light. Electromagnets serve for guidance and focusing of the particles.

3. Synchrotron
3. Synchrotron
Coming from the linear accelerator, twelve 30° magnet force the ion beam on a circular path. Within one second and during about 1 million circuits, the velocity of the ions is increased to more than 70% of speed of light. The accelerating process can be stopped at different speed levels or energies. In this way, the penetration depth of the beam into the tissue can be controlled.
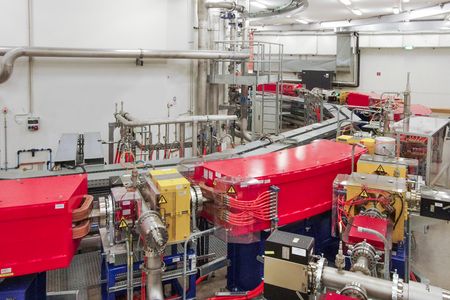
4. Beam guidance
4. Beam guidance
On the way to the treatment unit: Within a vacuum tube, the therapy beam is guided and focused by electromagnets and finally reaches the desired treatment site.



